Sanatan Articles
Satyaagrah
Written on
Satyaagrah
Written on
Satyaagrah
Written on
Satyaagrah
Written on
Satyaagrah
Written on
JOIN SATYAAGRAH SOCIAL MEDIA
How Nehru had laid blue print of Indira Gandhi inheriting his PM post
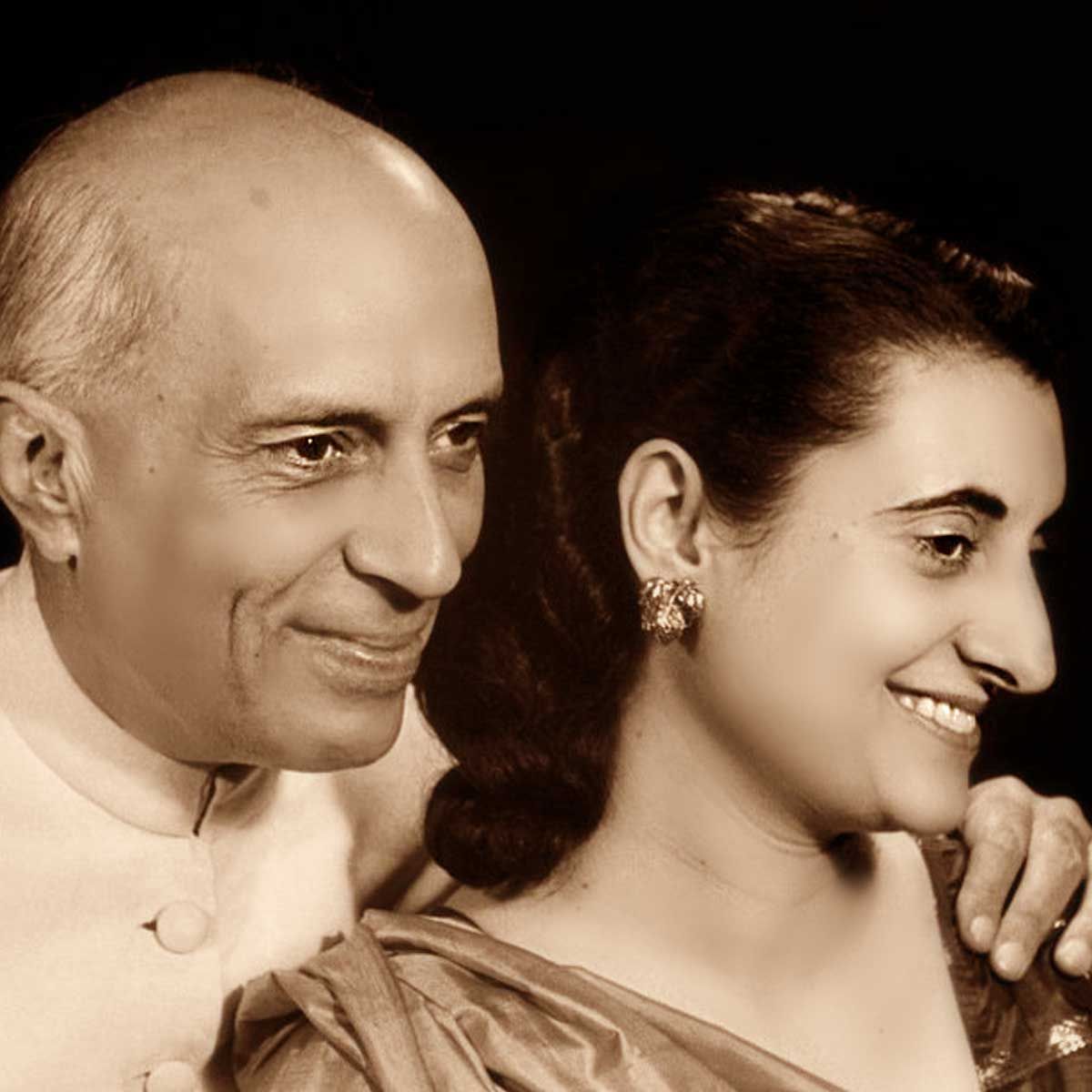

Indira Gandhi was one of the most prominent leaders who led the country. She was known for many things. Indira Gandhi was an astute and shrewd politician who waded her way through the political corridors dominated by males through sheer grit and what some say as ruthlessness. The way she handled foreign policy to the role India played in the Bangladesh liberation war of 1971 under her rule, Indira Gandhi has left an indelible mark on India's post-independence history.
From where did Indira get her political lessons or who groomed her to enter politics? Was it Nehru or were it the circumstances? These questions have been debated for a long time. Some even say that Indira becoming the Prime Minister was the beginning of the dynastic politics in India because after Indira her son Rajiv Gandhi became PM. In 2019 Lok Sabha elections, the Congress projected her grandson Rahul Gandhi as the PM candidate. So where did it all start and did Nehru really want it to be this way.
‘Who After Nehru’? This was one key question which became the headline in almost all national and international newspapers after the demise of Jawaharlal Nehru, the first Prime Minister of the country on May 27, 1964. The death of India’s first Prime Minister Jawaharlal Nehru stimulated debates, both inside and outside the Indian subcontinent, on India’s future in a post-Nehruvian world. However, after the death of Jawaharlal Nehru, Lal Bahadur Shastri took over as the Prime Minister of India.
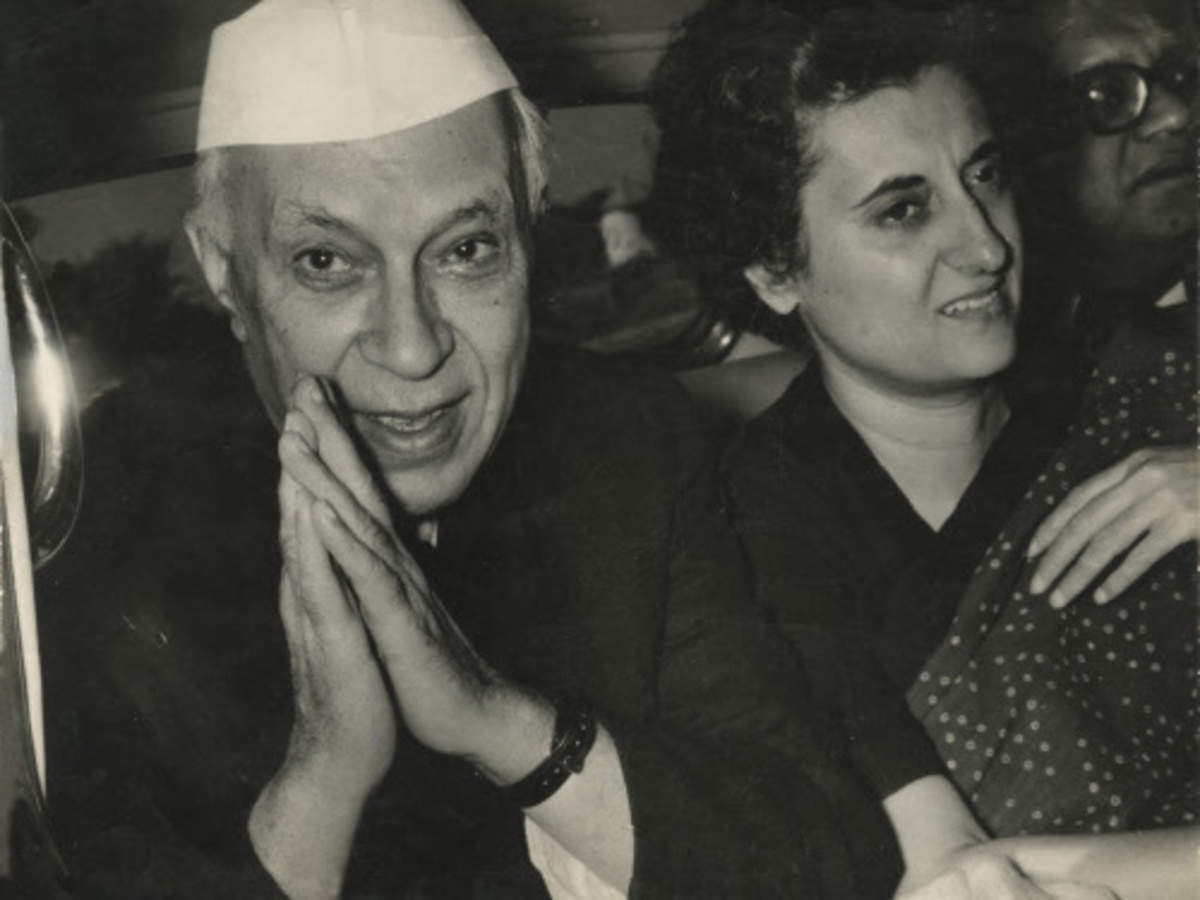 |
During his nineteen months as PM, one got many glimpses of his unique style of leadership. Much of these months were spent in settling down and dealing with one crisis after another. Just as Winston Churchill was known as the ‘War Time Prime Minister’ in Britain, it would be only just to refer to Lal Bahadur Shastri as the Prime Minister who helped India navigate through its most difficult period in the Post-Independence era.
From calming the violent anti-Hindi agitation that erupted across the southern states to take the first steps in resolving India’s biggest food shortage by promoting the Green Revolution and convincing people to voluntarily give up one meal so that the food saved could be distributed to the affected populace and the White Revolution (Amul cooperative), Shastri led India through its most crisis-ridden period.
Shastri’s mandate to become Prime Minister was not easy. After Jawaharlal Nehru’s death, there was a fragmented consensus within the Congress party about his ability to lead the nation. After India’s crushing defeat in the Sino-Indian border war of 1962 and a severe food crisis which followed, India’s morale had fallen. Given these developments, India appeared vulnerable. In 1965 Pakistan wanted to take advantage of this ‘weak leadership’. The assumption was that a relatively unstable India would not involve itself in another full-scale war. And it appeared to be a perfect moment for Pakistan to make another effort to seize Kashmir.
Lal Bahadur Shastri surprised many with his wartime leadership that saw the Indian government openly declaring that they will not tolerate another attempt by Pakistan to snatch Kashmir by force.
 |
How vulnerable India’s situation was at that time can be ascertained from what Chakravarti Rajagopalachari informally called Rajaji or C.R said after the death of Jawaharlal Nehru:
“The greatest danger now facing India is the failure to effect cordial relationship with Pakistan or neglect of this important issue. The consequent weakness of the sub-continent against communist aggression should be the first concern of all thinking men India and Pakistan. I also feel that on the economic plane the greatest danger now is a stubborn continuation of the policy of expensive taxation and far too ambitious Soviet-style of Planning, leading to inflation. The vital element of the population, on which depends democracy, is crushed between inflation and taxation. Put in general terms, the greatest danger now would be the failure of the new Government to realize the need for a change of policy in spite of admiration and worship paid to the memory of the late Prime Minister”.
Prime Minister’s election after Nehru’s death
However, Nehru had not anointed a successor before his death, and the battle for supremacy was on with Kamaraj pulling the strings under his famous “Kamaraj Plan” to reinvigorate the party.
It is pertinent to note here that over the years many old guards and the young brigade of the Congress party has used the selection of Lal Bahadur Shastri for the PM post to contend that the party does not necessarily belive in ‘dynasty politics’ as in 1964, Lal Bahadur Shastri succeeded Nehru as India’s Prime Minister, not Indira Gandhi. However, we all know that this argument does not hold waters. It is obvious that this sophistry given by the Congress supporters has been used only to cover up the truth of the dynasty politics prevailing in this political party.
After Nehru’s death, the then Congress leadership was divided between Jayprakash Narayan, Morarji Desai and Indira Gandhi for the post of India’s PM. It is widely believed that on one hand while Morarji Desai was not ready to accept the post, Kamaraj himself did not want to hand over the reins of the country to the old and established guard-Morarji Desai. It is widely believed that this was Kamaraj’s (and Nehru’s) plan to weed out the old guard, leaders such as Morarji Desai, Lal Bahadur Shastri, Jagjivan Ram, Biju Patnaik and S.K. Patil, many of who could stand in the way of Indira Gandhi’s eventual elevation as PM.
The plan succeeded. When Nehru passed away, Shastri was elected, mainly because Kamaraj backed him against Desai. And, when Shastri died suddenly, Indira became PM.
In fact, Jawaharlal Nehru always wanted his daughter Indira Gandhi to be his successor. No one else but Lal Bahadur Shastri himself said this to the late journalist Kuldip Nayar. Kuldip Nayar has mentioned this in his book Beyond the Lines that Shastri had once told him that Nehru wanted to see Indira as his political successor.
 |
The grooming of Indira Gandhi was so perfect that she started talking and giving speeches just like her father. In the book Six Thousand Days, Amiya Rao and B G Rao, write that six months after she was nominated to the Working Committee, Nehru resigned from the powerful Central Parliamentary Board and nominated Indira Gandhi. This was the committee which picked the candidates for elections and decided on the political fate of thousands of Congressmen and women.
The book 'Six thousand days: Jawaharlal Nehru, Prime Minister' also argues that Nehru had moulded the party to accept Indira Gandhi as the prime minister. "He skillfully removed all the strong contenders to the post like Jagjivan Ram and Morarji Desai by making statements that Congress does not encourage people getting addicted to power. He kept people like Gulzarilal Nanda, who would not be a strong contender, but would be a stop-gap arrangement. All of Nehru's actions indicated that he was promoting the dynasty, but it is strange that modern historians have no recollection of all these events," the book says.
Kuldip Nayar had written that in the moments just after Shastri’s demise in Tashkent: “Swaran Singh turned to me and asked, ‘Kuldip, who do you think could be the next prime minister?’ I repeated to him what Shastri had himself told me a few months earlier, ‘If I die in the next two years, my successor will be Indira Gandhi. If I survive, it will be YB Chavan’.
Kuldip Nayar also revealed in his book that Lal Bahadur Shastri was not Nehru’s first choice for his successor.
In fact, the Nehru-Gandhi’s disapproval to Shastri rising to power can be gauged from the fact that Gandhi dynasty has tried to virtually delete Shastri’s name from India’s history. History has it that Indira Gandhi was not in favour of building Shastri’s samadhi in Delhi after his death.
Kuldip Nayar has written in his book that only after Lalita Shastri, wife of Shastri Ji, threatened to fast unto death, did Indira Gandhi change the decision and build a samadhi of Shastriji in Delhi.
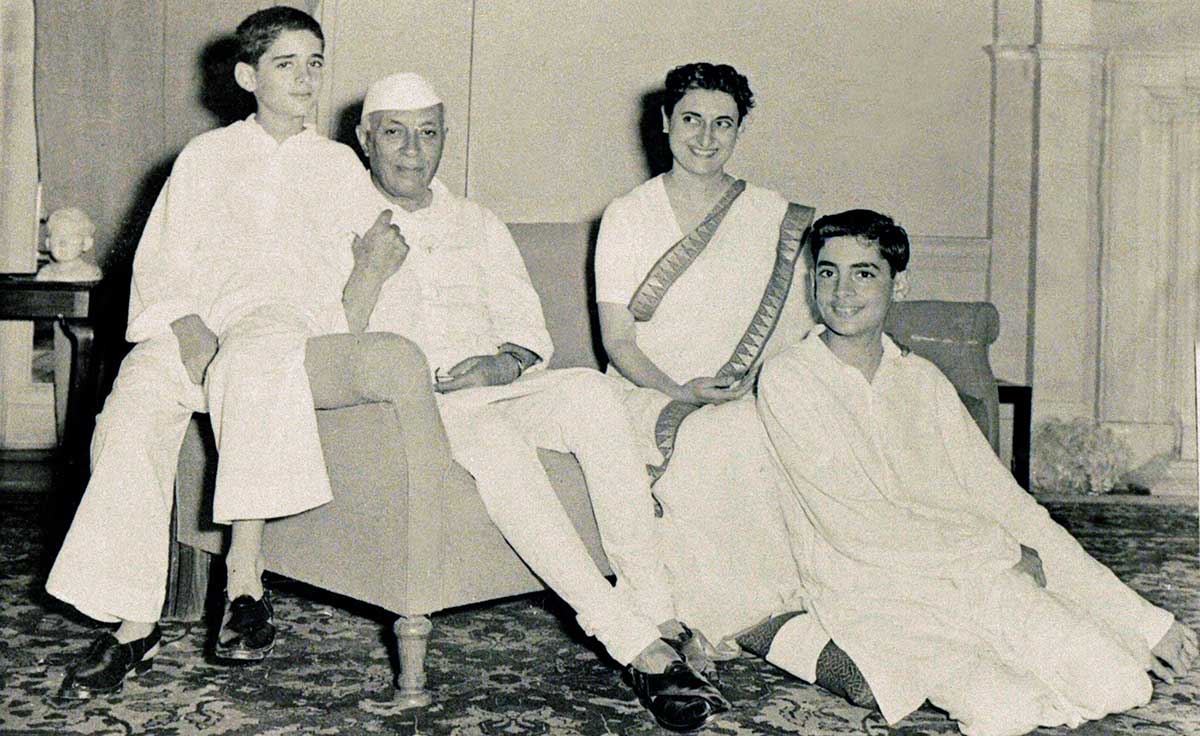 |
The making of Indira Gandhi-the Prime Minister
Indira Gandhi was the daughter of Jawaharlal Nehru, the first prime minister of India. She served as prime minister from January 1966 to March 1977 and again from January 1980 until her assassination in October 1984, making her the second longest-serving Indian prime minister after her father.
But her road to power and politics was carefully crafted by Jawaharlal Nehru. He shrewdly elevated her to the position of the President of the Congress, in 1959, which marked her entry into politics and the first phase of dynastic politics in Congress. After Nehru’s death, Indira Gandhi was sent to the Rajya Sabha and made a cabinet minister in the Shastri government. Soon after the death of Lal Bahadur Shastri, Indira Gandhi became the Prime Minister of the country.
Those who claim that Indira Gandhi’s name was not even discussed for the next Prime Minister candidature after Nehru should read the ‘New York Times’ report in which on January 9 1964, just 5 months before Nehru’s death, Indira Gandhi was mentioned as a possible successor to Nehru.
In fact, DP Mishra, a senior Congress leader who closely witnessed power transitions after Nehru’s and Shastri’s deaths explains Nehru’s game plan. The strategy evolved by Nehru was to groom his daughter for PM-ship, then eliminate Morarji Desai and Jagjivan Ram, two ambitious, competent and influential rivals, and finally place both the Govt and the Congress in the hands of men who, even if tempted by premiership, would be easily removable by his daughter. Through the Kamraj plan, he (Nehru) removed Desai and Jagjivan Ram from his government, got Kamaraj elected as Congress President and left the government in the hands of Gulzarilal Nanda, TT Krishnamachari and Lal Bahadur Shastri.”
 |
 |
When Alexei Kosygin called Lal Bahadur Shastri ‘super Communist’
India’s second Prime Minister- Lal Bahadur Shastri, the exemplary stalwart and an impeccable leader, was also known to be considerate toward those working in his team. On 3rd January 1966, he left for Tashkent hoping for a long-term peace solution with Pakistan. Tashkent was very cold at that time of the year and Shastriji was carrying his usual Khadi woollen coat. Russian leader Alexei Kosygin realised that the coat he wore was not warm enough to fight the snowy winter winds of Central Asia.
Kosygin wanted to present a Russian overcoat to Shastriji but was not sure how to do so. Finally, at a function, he gifted a Russian coat to the Prime Minister hoping that he would wear it while in Tashkent. Next morning, Kosygin noticed that Shastriji was still wearing the Khadi coat. Hesitantly, Kosygin asked the Prime Minister if he liked the overcoat. Shastriji said: “It is really warm and very comfortable for me. However, I have lent it to one of my staff members who was not carrying a good woollen coat to wear in this severe winter. I will surely use your gift during my future trips to cold countries”.
Kosygin narrated this incident during his welcome address at a cultural programme organised in honour of the Indian Prime Minister and the Pakistani President. Kosygin remarked: “We are communists but Prime Minister Shastri is a Super Communist”.
There are many aspects related to Shastriji’s life and values, which make him a cut above all the politicians of any time and age, but it is not easy to pen down the stalwart’s personality in a few words.
Whether it be the incident where the former PM took a loan of Rs 5,000 from PNB to buy a fiat car or be it tactfully handling the food crisis in India or being refered to ‘super communist’ due to his compassion for fellow workers, Lal Bahadur Shastri emerged as a leader with his own distinct style and approach.
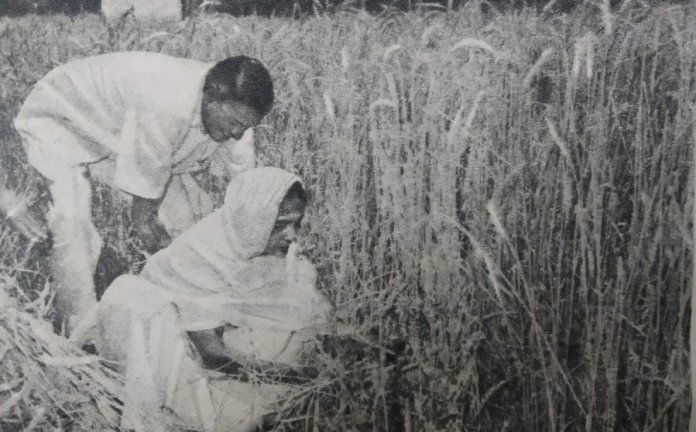 In this picture, 3 months after Shastriji’s death, his wife Lalitha Shastri is harvesting this crop. Shastri ji had grown this crop at 10 Janpath to inspire the countrymen during the food crisis. |
Today on his birth anniversary, Shastriji would be remembered as a people’s person who dealt with all individuals with trust, tact and transparency. The trust quotient that Shastri evoked was extremely high. One would not come across examples of his letting down a colleague. His mentors reposed implicit faith in him as did his peers and followers.
It’s extremely unfortunate that Lal Bahadur Shastri departed from the scene much before the country could truly benefit from his full potential.
References:
oneindia.com - By Vikas Sv
opindia.com - Ashish Nautiyal
 Support Us
Support Us
Satyagraha was born from the heart of our land, with an undying aim to unveil the true essence of Bharat. It seeks to illuminate the hidden tales of our valiant freedom fighters and the rich chronicles that haven't yet sung their complete melody in the mainstream.
While platforms like NDTV and 'The Wire' effortlessly garner funds under the banner of safeguarding democracy, we at Satyagraha walk a different path. Our strength and resonance come from you. In this journey to weave a stronger Bharat, every little contribution amplifies our voice. Let's come together, contribute as you can, and champion the true spirit of our nation.
 |  |  |
| ICICI Bank of Satyaagrah | Razorpay Bank of Satyaagrah | PayPal Bank of Satyaagrah - For International Payments |
If all above doesn't work, then try the LINK below:
Please share the article on other platforms
DISCLAIMER: The author is solely responsible for the views expressed in this article. The author carries the responsibility for citing and/or licensing of images utilized within the text. The website also frequently uses non-commercial images for representational purposes only in line with the article. We are not responsible for the authenticity of such images. If some images have a copyright issue, we request the person/entity to contact us at This email address is being protected from spambots. You need JavaScript enabled to view it. and we will take the necessary actions to resolve the issue.
Related Articles
- Father of the Nation! Absolutely not. Mohandas Karamchand Gandhi was not the father of the nation either officially or otherwise
- How Communists betrayed India - 100 Years of Russian Revolution
- Can Communism and Democracy Coexist - 100 Years of Russian Revolution
- Ghost from the past: Unseen picture of Nehru voting in favour of partition of India goes viral
- How Nehru's Govt helped China in conquering Tibet and let go of it's centuries old friend
- Prophecies of Jogendra Nath Mandal getting real after seventy years of his return from Pakistan
- On 16th Aug 1946, during Ramzan's 18th day, Direct Action Day aimed to provoke Muslims by mirroring Prophet Muhammad's victory at Badr, Gopal 'Patha', the Lion of Bengal, heroically saved Bengali Hindus & Calcutta from a planned genocide, altering history
- Depth of Soviet penetration in Indian media is exposed through declassified CIA document from 2011
- Harmonizing Nathuram Godse: Why India should move beyond denouncing him, a man who altered the course of not only the politics of the country but the very history of the Hindu Civilisation and, by extension, the world at large
- Indira Gandhi’s bahu published intimate photos of Jagjivan Ram’s son in her magazine: This 'Saas-Bahu ki Saajish' mothered India’s first major political sex scandal which cost Jagjivan his political career
- Mysterious death of Pandit Deen Dayal Upadhyaya, whose growing popularity was a threat to Congress
- How undisciplined Indira Gandhi when expelled from Congress Party by 'Syndicate', divided the party into two: 12 November 1969
- Saam Daam Dand Bhed: How Indira and Sanjay Gandhi pulled off the Maruti scam
- Operation Polo: When India annexed Hyderabad from the Nizam and Razakars, the suppression of Hindus and the role of Nehru
- When Secular Nehru Opposed Restoration Of Somnath Temple - The Somnath Temple treachery





















